Table Of Content
If the RMRP pathogenic variants have not been identified in an affected family member, prenatal diagnosis for a pregnancy at increased risk may also be possible through fetal ultrasound studies at weeks' gestation. Newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) using detection of T cell receptor excision circles is able to identify some individuals with CHH prior to recognition of other findings [Kwan et al 2013]. The major radiographic features in infancy include shortened tubular bones. The radiographic features in children and adults include short, flared and irregular metaphyses of tubular bones. These changes are typically more prominent in the knee region than at the hips. The fibula is often disproportionately long, most notably at the ankle, and can lead to ankle varus.
Cartilage hair hypoplasia: characteristics and orthopaedic manifestations
In these 2 patients, the diagnosis was done on genetic basis because they were very young and had no characteristics of skeletal dysplasia. Mutations in RMRP were found in 12 patients of whom 9 were compound heterozygotes. There are irregular cystic radiolucencies in the metaphyses with extension into the diaphyses. Abnormal epiphyseal shape occurs, seemingly as a consequence of the deformed metaphyseal region.
Ribosome biogenesis in skeletal development and the pathogenesis of skeletal disorders
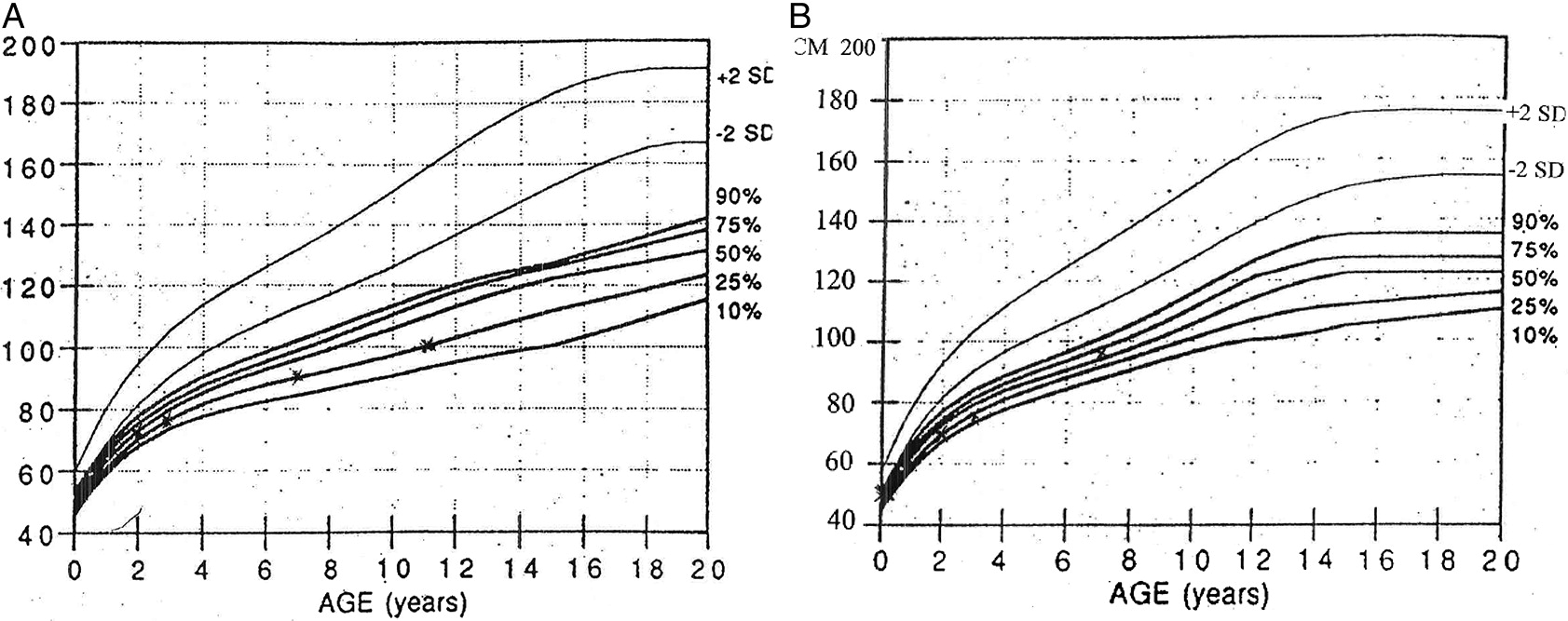
McKusick et al. [1, 2] and Coupe and Lowry [61] examined the hair grossly, microscopically, and in diameter. The hair has been demonstrated to be diminished in caliber and lacks a pigmented core, a finding also observed by van der Burgt et al. [3]. The hands are short and “pudgy” with marked excessive joint laxity, particularly of the metacarpal, phalangeal, and interphalangeal joints [1, 62]. Bowing of the lower extremities and disproportionate length of the fibula compared to the shortened tibia is consistent, although unproven as the cause of the ankle varus, resulting in ankle varus from relative fibular overgrowth (Fig. 1). The authors examined charts and/or radiographs in 135 cases of CHH.
Mutation detection in RMRP
Researchers from participating institutions use the database to search for and invite patients or healthy volunteers who meet their study criteria to participate. One of the defining features of cartilage hair hypoplasia is the presence of fine, sparse hair. Individuals usually have hair that is lighter in color than their family members. This results in a lighter appearance since the core contains some of the pigments that contribute to hair color, as well as thinner strands of hair. If a diagnosis remains unknown despite extensive efforts by your PCP and specialists, it can be challenging to know what kind of expert you may need or where to find one.
Find Cartilage Hair Hypoplasia Expertise at Nemours
The B-lymphocyte count was low in 2 patients (pt 2 and pt 11); the data of 1 patient (pt 11) are not available because he received Rituximab before the evaluation. Levels were normal in 7 patients, and in 2, all fractions were reduced. Isolated IgG deficiency was present in 1 patient and combined IgG and IgA deficiency was observed in 1 patient. Pt 11 was under immunoglobulin substitution after Rituximab administration. With regular medical care, most kids with cartilage hair hypoplasia can live a full, healthy life. We offer care for children with cartilage hair hypoplasia at Nemours Children’s Health, Pensacola and our hospital affiliate, West Florida Healthcare, with outpatient and follow-up appointments also available at select Nemours specialty care locations.
Sequence analysis detects variants that are benign, likely benign, of uncertain significance, likely pathogenic, or pathogenic. Variants may include nucleotide substitution and small intragenic deletions. For issues to consider in interpretation of sequence analysis results, click here.
To establish the extent of disease and needs of an individual diagnosed with a CHH-AD spectrum disorder, the evaluations summarized in Table 3 (if not performed as part of the evaluation that led to the diagnosis) are recommended. RMRP is not translated into a protein; thus, genotype-phenotype correlation depends on the position of the pathogenic variant in the transcript and the proposed effect on transcript folding and RNA-protein interaction (see Molecular Genetics). Depending on the degree of curvature, it can be managed through observation, bracing, or surgery. Important to note that this gene is non-coding, therefore mutations could be missed in whole exome sequencing. It is more common in families with Old-world Amish and Finnish ancestors. Among Amish people, the incidence is approximately 1.5 in 1000 live births, and in Finland, it is 1 in 18,000 to 23,000.

Immunodeficiency
These high age estimates are in keeping with the distribution of the mutation, which also suggests an ancient introduction of this mutation into the Finnish population. The overall survival rate was 10/16 (63%) and 10/13 (80%) for the patients receiving matched sibling transplants or unrelated donor transplants. These results are in keeping with the European results for other T-cell immune deficiency, and highlight the poor results from haploidentical HSCT, but encouraging results when well-matched donors are used. Donor chimerism was assessed in 12 patients, and was measured in whole blood in some centers and as lineage-specific chimerism in other centers.
Patients with these types of deficiencies have some defect in their T-cell (cellular) immune system, resulting in a different spectrum of infection problems than those individuals with typical antibody deficiency. These include deep-seated bacterial infections, viral and fungal infections, tuberculosis, and other mycobacterial infections. Cellular immunodeficiencies are usually more difficult to treat and may need cellular reconstitution via hematopoietic stem cell transplantation or gene therapy. Several nonskeletal issues are of considerable importance in association with CHH. In the McKusick series, a few patients had evidence of aganglionic colon, two patients died of varicella, and three others had had virulent infections with varicella.
Verne Troyer: Late Actor Had Cartilage-Hair Hypoplasia and Faced Adversity - AOL
Verne Troyer: Late Actor Had Cartilage-Hair Hypoplasia and Faced Adversity.
Posted: Sun, 18 Feb 2024 19:05:58 GMT [source]
Affected individuals with the most severe immune problems are considered to have severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). People with SCID lack virtually all immune protection from bacteria, viruses, and fungi and are prone to repeated and persistent infections that can be very serious or life-threatening. These infections are often caused by "opportunistic" organisms that ordinarily do not cause illness in people with a normal immune system.
See Management, Evaluation of Relatives at Risk for information on evaluating at-risk relatives for the purpose of early diagnosis and treatment. See Genetic Counseling for issues related to testing of at-risk relatives for genetic counseling purposes. Supportive care to improve quality of life, maximize function, and reduce complications is recommended. This ideally involves multidisciplinary care by specialists in relevant fields (see Table 4).
This review focuses on the pathogenesis, clinical course and management of CHH. Cartilage-hair hypoplasia (CHH) is a rare autosomal recessive disease caused by mutations in the RMRP gene. Beside dwarfism, CHH has a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations including variable grades of combined immunodeficiency, autoimmune complications, and malignancies. Because long-term experience in larger cohorts of CHH patients after HSCT is currently unreported, we performed a European collaborative survey reporting on 16 patients with CHH and immunodeficiency who underwent HSCT.
RNase MRP also forms a complex with telomerase reverse transcriptase catalytic subunit (encoded by TERT), which may play a role in cellular senescence [Maida et al 2009]. If recurrent infections are present, milder forms of Schimke immunoosseous dysplasia may be confused with cartilage-hair hypoplasia [Baradaran-Heravi et al 2008]. Congenital neutropenia that occurs as part of a syndrome can be caused by pathogenic variants affecting glucose metabolism or lysosomal function. The most frequently observed cancers are non-Hodgkin lymphoma, followed by squamous cell carcinoma, leukemia, and Hodgkin lymphoma; non-aggressive basal cell carcinoma was also common. There are isolated reports of uterine carcinoma and vocal cord carcinoma [Kostjukovits et al 2017b].
Amish migration has resulted in many cases seen in other states, particularly in Ohio at present [1, 2]. Several surgical procedures were performed on patients with angular and/or rotational deformity. In this series of patients, roughly 43 % had undergone surgical realignment of the lower extremities. The ages at surgery ranged from 2 to 27 years, with an average of 11.7 years and mean of 14.5 years.
Despite significant short stature in women with CHH and other potential CHH-related effects on pregnancy outcome, most pregnancies lead to a term cæsarean section delivery. Fetal growth is generally unaffected; therefore, planned cæsarean section should be considered in term pregnancies due to cephalopelvic disproportion [Holopainen et al 2020]. Individuals with normal hair and metaphyseal dysplasia, called metaphyseal dysplasia without hypotrichosis (MDWH), were reported by Bonafé et al [2002].

No comments:
Post a Comment